How is Hydrogen Produced?
5 min read
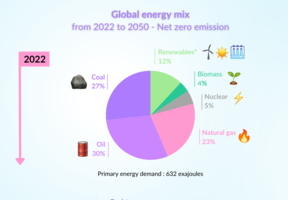
is the most abundant element in the natural world, but it is almost always combined with other elements, so it has to be isolated. The problem is that 95% of hydrogen is currently produced using processes that emit CO2 and therefore contribute to , including steam methane reforming and gasification. Water electrolysis separates hydrogen and oxygen atoms without generating any CO2 emissions, but the process is expensive. Researchers are working on other sustainable methods using microorganisms and photoelectrochemical cells.
How is Hydrogen Produced?
Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical element in the universe.
But it is almost always combined with other elements. Example: water (H2O) = hydrogen (H) + oxygen (O)
To use pure hydrogen in a cell or car engine, the element needs to be isolated. The most common method is steam reforming. Steam (H2O) reacts with to separate the carbon (C) atoms from the hydrogen (H) atoms. The reaction yields dihydrogen (H2) + carbon dioxide ( )
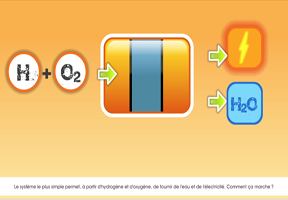
The same result is achieved with the charcoal gasification process, which consists in burning charcoal in a very high-temperature reactor. Another method: water electrolysis. An electric current is used to decompose water (H2O) into: dihydrogen (H2)/dioxygen (O2)
However, 95% of hydrogen is produced from fossil fuels or wood.
So we need to find alternatives for producing hydrogen, and ensure that these alternatives emit little-to-no greenhouse gas.
- #1 Photosynthetic microorganisms, which can produce hydrogen using sunlight.
- #2 Photoelectrochemical cells, electric components submerged in water and exposed to light to produce bubbles of dihydrogen and dioxygen.
- #3 Thermochemical decomposition of water. Heated to a high temperature, the water
decomposes and releases the dihydrogen.
Summary:
- In nature, hydrogen is always combined with another element. To use pure hydrogen, the element needs to be isolated.
- 3 methods:
- Steam reforming with steam and methane (CH4).
- Charcoal gasification, which consists in burning charcoal.
- Water electrolysis. - However, 95% of hydrogen is produced from fossil fuels or wood.
- More sustainable alternatives do exist: photosynthetic microorganisms and photoelectrochemical cells.